一位科學家與教育工作者對藤材危機的觀點
今天,在與一位深切關注環境議題的科學家和教育工作者討論後,我深感有必要分享關於藤這種材料的嚴峻現況。藤不僅是手工藝品和家具的原料,更是我們童年記憶中呼拉圈的重要組成部分。
然而,數據顯示,藤資源正遭受前所未有的威脅。這不僅影響產業發展,更對全球生態系統和永續教育敲響了警鐘。
要點
- 藤製品市場具有巨大潛力,但藤資源正面臨嚴峻挑戰。
- 數據分析揭示了藤產業的供應鏈集中、資源稀缺和產業挑戰等問題。
- 藤呼拉圈的案例反映了藤資源稀缺對消費品的影響。
- 永續教育對於培養下一代的環保意識和行動力至關重要。
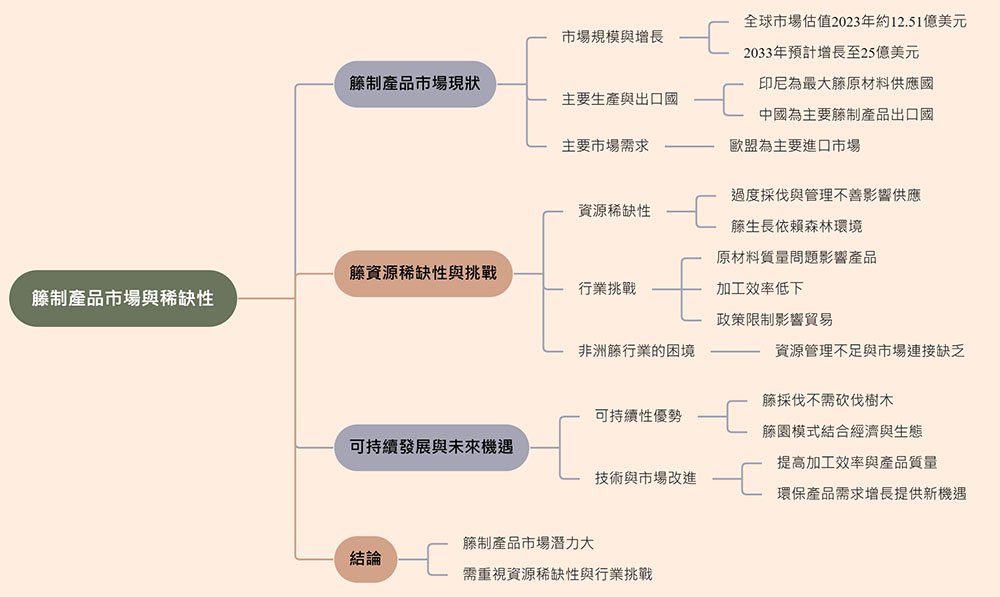
數據分析:藤市場的現況與挑戰
讓我們從數據的角度,深入剖析藤產業的現況與挑戰:
1. 全球市場規模與增長
- 市場估值: 根據市場研究報告,2023 年全球藤製產品市場估值約為 12.51 億美元。
- 預期增長: 預計到 2033 年,市場規模將增長至 25 億美元,年複合增長率(CAGR)約為 5%。
- 藤家具市場: 預計 2025 年達到 9.6 億美元,2030 年增長至 12.2 億美元,CAGR 超過 5%。
這些數據表明,藤製品市場具有巨大的增長潛力,但同時也面臨著原材料供應的壓力。
2. 主要生產與出口國
- 印尼: 作為全球最大的藤原材料供應國,印尼佔據了全球供應的 80%。
- 中國: 中國是藤製產品的主要出口國之一,尤其在工業化藤產品和編織藤產品方面具有優勢。
這種高度集中的供應鏈,使得藤產業更容易受到特定地區政策和環境變化的影響。
3. 主要進口市場
- 歐盟: 歐盟是藤製產品的主要進口市場,佔全球進口量的 38%。
- 歐盟對環保和可持續產品的需求,為藤產業提供了機遇,但也對藤的來源和生產過程提出了更高的要求。
4. 資源稀缺性
- 過度採伐: 由於市場需求旺盛,許多地區存在過度採伐藤資源的現象,導致資源枯竭。
- 森林砍伐: 藤的生長依賴健康的森林生態系統,森林砍伐直接威脅到藤的生存。
- 保護狀態: 儘管藤目前被列為“無危”(Least Concern),但其生存狀況正日益受到威脅。
5. 產業挑戰
- 原材料質量: 市場上存在藤原材料質量參差不齊的問題,影響最終產品的品質。
- 加工效率: 藤的加工過程仍以手工為主,效率較低,且缺乏標準化的質量控制。
- 政策限制: 在某些國家,藤仍被歸類為森林產品,受到相關關稅和出口限制的影響。
藤的生態價值與永續性
儘管面臨挑戰,藤作為一種非木材林產品(NTFP),具有獨特的生態價值和永續性:
- 生長特性: 藤主要生長在次生森林中,需要充足的光照。
- 永續採伐: 藤的採伐不需要砍伐樹木,因此對森林生態系統的影響較小。
- 碳封存: 藤的快速生長有助於碳封存,對減緩氣候變化具有潛在貢獻。
案例分析:藤呼拉圈 – 以小見大
隨著時間的推移, 藤呼拉圈的變化反映了更廣泛的藤資源稀缺性和產業挑戰。
- 原材料短缺: 藤資源的減少迫使製造商尋找替代材料或減少藤的使用量,導致呼拉圈的耐用性和品質下降。
- 生產成本上升: 原材料價格上漲和加工效率低下,導致藤呼拉圈的生產成本增加,最終反映在售價上。
永續教育的迫切性:從藤的案例出發
藤的案例為我們敲響了警鐘,凸顯了永續教育的迫切性。我們需要讓下一代認識到:
- 資源有限: 地球上的資源並非取之不盡、用之不竭。
- 生態平衡: 人類活動對生態系統具有深遠影響。
- 永續發展: 我們需要尋求經濟發展與環境保護之間的平衡。
藤的生態價值:不只是呼拉圈
藤,這種看似不起眼的植物,其實對森林生態系統至關重要。
- 生長: 藤主要生長在次生森林中,需要充足的光照。
- 永續性: 採收藤不需要砍伐樹木,因此被視為一種可持續的非木材林產品。
這意味著,合理利用藤資源,不僅可以滿足我們的生活需求,還可以保護森林,實現雙贏!
與孩子們的對話:從呼拉圈談起
場景: 在一堂自然課上,我拿著一個藤呼拉圈走進教室。
我: 「孩子們,你們知道這是什麼嗎?」
孩子們: 「呼拉圈!」
我: 「沒錯!但你們知道它是用什麼做的嗎?」
孩子們: (七嘴八舌)「塑膠?」「木頭?」
我: 「很多呼拉圈是用一種叫做『藤』的植物做的。藤很有趣,它生長在森林裡,但採收它不需要砍樹喔!」
孩子們: 「哇!好神奇!」
我: 「是啊!但現在,藤越來越少了,因為很多人沒有好好保護森林。如果我們不珍惜藤,以後可能就沒有呼拉圈玩了。」
孩子們: 「那我們可以做些什麼呢?」
我: 「這就是我們今天要學習的重點!」
藤的稀缺性:問題與挑戰
儘管藤具有永續性,但過度採伐和資源管理不善,導致藤資源的供應壓力日益增加。
- 過度採伐: 為了滿足市場需求,許多地區過度採伐藤,導致藤資源枯竭。
- 森林砍伐: 藤的生長依賴森林環境,森林砍伐直接威脅到藤的生存。
- 品質問題: 市場上存在原材料質量不穩定的問題,如節間過短、顏色不均等。
- 加工效率低: 藤的加工仍以手工為主,效率較低
永續教育:從藤開始
藤的困境,給我們上了一堂寶貴的永續教育課。我們可以從以下幾個方面入手:
- 認識藤: 了解藤的生態價值、生長特性和用途。
- 珍惜資源: 培養節約資源、愛護環境的意識。
- 支持永續產品: 選擇購買來自可持續來源的藤製品。
- 參與行動: 參與植樹造林、保護森林等環保活動。
教學實踐:將藤融入課程
身為教育工作者,我們可以將藤的議題融入課程中:
- 自然課: 介紹藤的生態知識,討論藤資源稀缺的原因和影響。
- 社會課: 探討藤產業的經濟價值,分析資源管理政策。
- 美術課: 利用藤或其他天然材料製作手工藝品,體驗永續設計。
- 體育課: 使用藤呼拉圈進行體能訓練,同時了解藤製品的文化意義。
提示與技巧
- 實地考察: 如果條件允許,帶孩子們參觀藤製品工廠或藤種植園,親身體驗藤的魅力。
- 跨學科合作: 與其他學科的老師合作,共同設計與藤相關的教學活動。
- 鼓勵創新: 鼓勵孩子們發揮創意,設計出更多環保、實用的藤製品。
- 分享經驗: 將你的教學經驗和成果分享給其他教育工作者,共同推動永續教育。
藤的警示提醒我們,永續發展不僅是一個口號,更是一個迫在眉睫的任務。
我們需要從數據出發,深入了解藤產業的現況與挑戰,並將永續教育融入各個層面。只有這樣,我們才能確保藤這種珍貴資源得以永續利用,並為下一代創造一個更美好的未來。
citation:
竹子和藤製的全球市場價值仍然充滿活力 - 根據INBAR編制的統計數據,竹子和藤製產品(國內和國際)的預測增長穩定,當時銷售大幅下降,數據揭示了需求已大大降低,尤其是從竹製製造的竹製產品中,造成了竹製量的生產2013年,國際竹和藤製產品的國際貿易為25億美元 - 最新的可用數字。
https://chinese.alibaba.com/product-detail/High-quality-export-Open-Weave-Rattan-10000008506648.html
https://felo.ai/search/S6NbT5Tcau7adTjSzN25Ub
世界上最重要的出口市場是歐盟,歐洲聯盟佔世界上竹子和藤進口的38%,世界上最大的生產國和竹式的出口國仍然是中國。基於可用的商業貿易的全球趨勢包括:工業化竹製產品的持續增長:從2009年的23%中,工業化竹子的比例從2009年$ 23%上升到了2009年的23%,這一數字為2009年$ 2009年2013;對織造產品的穩定需求:與糧農組織和中國的海關部門合作,竹子和藤製產品的比例保持在35%。 “僅中國就預測到2020年的國內竹和藤製市場將翻了一番,並越來越多地認識到竹子的'綠色'資格,在未來的幾年中,竹子和藤的貿易很有可能會繼續保持穩定,並且很可能會增長。”